Delving into the realm of architectural safety standards in accident-prone zones, this piece sets the stage for a deep dive into the crucial aspects that shape our built environment. From preventing disasters to ensuring public safety, let’s unravel the intricacies of this vital topic.
Importance of Architectural Safety Standards in Accident-Prone Zones
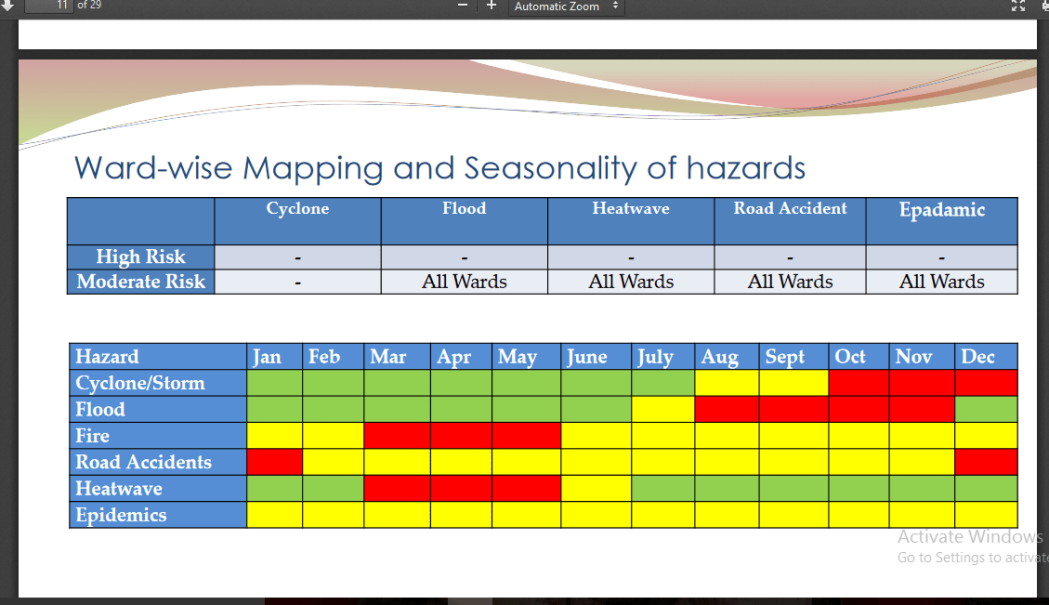
Architectural safety standards play a crucial role in ensuring the well-being of individuals residing in or frequenting accident-prone zones. These standards are specifically designed to mitigate risks and prevent potential disasters by incorporating safety measures into the design and construction of buildings and infrastructure.
Prevention of Accidents
By adhering to strict safety standards, many accidents can be prevented in accident-prone zones. For example, buildings constructed in earthquake-prone areas need to follow specific guidelines to ensure structural integrity and reduce the risk of collapse during seismic activities. Similarly, proper fire safety measures in high-risk areas can prevent devastating fires from spreading and causing harm to occupants.
Impact on Public Safety and Infrastructure
The consequences of not following safety standards in accident-prone zones can be catastrophic. Inadequate structural design or lack of safety measures can result in loss of lives, injuries, and extensive damage to buildings and infrastructure. This not only endangers the individuals present in these areas but also puts a strain on emergency response systems and the overall resilience of the community.
Factors Influencing Architectural Safety Standards
When it comes to developing safety standards in accident-prone zones, several key factors play a crucial role in shaping the architectural designs to ensure the safety of individuals in those areas.Geographical location and environmental conditions have a significant impact on safety standards.
For instance, regions prone to earthquakes will require buildings to be designed with seismic-resistant features to withstand tremors. Similarly, areas susceptible to hurricanes or typhoons will need structures that can withstand high winds and flooding. Understanding the specific risks posed by the location and climate is essential in determining the safety requirements for architectural designs.Historical data and case studies also play a vital role in determining safety standards.
By analyzing past accidents, building failures, and natural disasters, architects and engineers can learn valuable lessons that can help improve future designs. This data-driven approach allows them to identify potential risks, vulnerabilities, and areas for improvement, leading to the development of more robust safety standards.
Impact of Geographical Location and Environmental Conditions
Geographical location and environmental conditions directly influence the safety standards required for architectural designs. For example, buildings in coastal areas need to be designed to withstand the impact of storm surges and flooding, while structures in earthquake-prone regions must incorporate seismic-resistant features.
Understanding the specific hazards posed by the location is crucial in developing effective safety standards to mitigate risks.
- Coastal Areas: Buildings in coastal regions need to be designed to withstand high winds, storm surges, and flooding. Elevated foundations, reinforced walls, and impact-resistant materials are often used to enhance the structural integrity of buildings in these areas.
- Mountainous Regions: Buildings in mountainous regions face risks such as landslides, avalanches, and rockfalls. Design considerations include slope stability, drainage systems, and the use of materials that can withstand extreme weather conditions.
- Urban Areas: Urban environments present unique safety challenges due to high population density and limited space. Safety standards in urban areas focus on fire protection, emergency evacuation routes, and structural stability to ensure the safety of residents and visitors.
Role of Historical Data and Case Studies
Historical data and case studies provide valuable insights into past accidents, building failures, and natural disasters, helping architects and engineers identify vulnerabilities and areas for improvement in architectural designs. By analyzing the root causes of failures and incidents, professionals can develop safety standards that address potential risks and enhance the resilience of buildings.
By learning from the mistakes of the past, architects and engineers can create safer and more resilient structures for the future.
Design Considerations for Architectural Safety in High-Risk Areas

When it comes to designing architectural structures in high-risk areas prone to accidents, specific considerations must be taken into account to enhance safety and mitigate potential risks. These design elements play a crucial role in ensuring the safety and well-being of individuals in these vulnerable zones.
Structural Resilience
In earthquake-prone areas, architectural designs should prioritize structural resilience to withstand seismic forces. This includes using flexible materials, incorporating base isolators, and implementing damping systems to reduce the impact of ground motion on buildings. Contrastingly, in flood-prone areas, structures should be elevated to prevent water damage and incorporate flood-resistant materials to minimize structural deterioration.
Emergency Exits and Evacuation Routes
Incorporating clearly marked emergency exits and well-defined evacuation routes is essential in high-risk areas. Buildings should have multiple exits strategically placed throughout the structure to ensure quick and safe evacuation in case of emergencies. Additionally, safe zones or assembly points should be designated outside the building to gather occupants away from potential hazards.
Safety Signage and Communication Systems
Installing safety signage and communication systems is vital for guiding individuals during emergencies in accident-prone zones. Clear and visible signage indicating evacuation routes, exit locations, and emergency procedures can help occupants navigate the building efficiently during high-stress situations. Communication systems such as intercoms or alarms should be in place to alert occupants of potential dangers and provide instructions for safe evacuation.
Compliance and Enforcement of Safety Standards
Ensuring compliance with safety standards in architectural design projects is crucial to prevent accidents and protect the lives of individuals in accident-prone zones. Compliance involves following specific guidelines, regulations, and codes set by authorities to ensure that buildings are constructed or renovated with safety as a top priority.
Enforcement Mechanisms for Safety Regulations
Successful enforcement mechanisms play a key role in promoting adherence to safety regulations in accident-prone zones. One effective approach is conducting regular inspections by qualified professionals to ensure that buildings meet the required safety standards. Additionally, implementing penalties for non-compliance can serve as a deterrent and encourage developers and architects to prioritize safety in their projects.
- Regular inspections by authorized personnel
- Penalties for non-compliance
- Education and training programs for architects and construction workers
Challenges in Monitoring and Enforcing Safety Standards
Monitoring and enforcing safety standards in existing structures located in high-risk areas present several challenges. One of the main difficulties is ensuring that older buildings are retrofitted to meet current safety standards, as this process can be costly and time-consuming.
Additionally, lack of awareness among building owners and occupants about safety regulations can hinder enforcement efforts.
- Cost and time constraints in retrofitting older structures
- Lack of awareness about safety regulations
- Resistance from building owners to implement safety upgrades
Last Point

As we conclude this exploration of architectural safety standards in accident-prone zones, it becomes evident that meticulous planning and adherence to regulations are paramount in safeguarding lives and infrastructure. By prioritizing safety measures, we pave the way for a more secure future in our built environment.
Question Bank
What are some key factors that influence the development of safety standards in accident-prone zones?
Factors such as geographical location, environmental conditions, historical data, and case studies play a crucial role in shaping safety standards for architectural designs in high-risk areas.
How can compliance with safety standards be ensured in architectural design projects?
Compliance with safety standards is typically ensured through rigorous inspections, adherence to building codes, and enforcement mechanisms that promote accountability among architects and builders.
Why is it important to incorporate emergency exits, evacuation routes, and safety signage in architectural designs for high-risk zones?
These elements are essential for ensuring swift and safe evacuation in case of emergencies, thereby reducing potential risks and enhancing overall safety in accident-prone areas.









